This patch fixes a collection of issues with widgets involved in text
editing:
* Fire widget.onChanged on EditableText value change:
The value of an EditableText is composed of the text value as well
as other editing-related data such as selection-related information.
Previously, widget.onChanged() was only called for updates via
updateEditingValue(). For pastes via a TextSelectionOverlay, updates
are signalled via _handleSelectionOverlayChanged(), which only ever
triggered widget.onSelectionChanged(), but not widget.onChanged().
Both updateEditingValue() and _handleSelectionOverlayChanged()
perform the value update via _formatAndSetValue(), which is where
this patch moves the widget.onChanged() call.
* Correctly update TextFormField value on edits via controller:
The textual value of a TextFormField exists in two locations:
1. FormField.value, as with all FormFields and subclasses.
2. TextEditingController.value associated with the TextField
underlying the TextFormField.
Previously, edits to the TextEditingController associated with a
TextFormField resulted in updates to the rendered TextField widget,
but did not update TextFormField.value. FormField.value is updated
via FormField's onChanged function, which is called from the
EditableText underlying the TextField underlying the TextFormField.
EditableText only fires onChanged when it receives changes from the
engine. It does not fire onChanged for changes made to the
underlying TextController, since the owner of the TextController is
the one making these changes and thus, already aware of them.
FormField, however, *does* need to listen to these changes to update
its value.
* Adds an initialValue parameter to the TextFormField constructor:
FormField's constructor already takes an initialValue parameter,
which specifies the initial value in the field, which is also the
value to which reset() returns the field.
Previously, TextFormField took its initial value from the controller
value (if a controller was passed in) or the empty string (if not).
This had the undesirable effect that calling reset() always resets
the value to the current value of the controller... i.e., does
nothing.
We now take an initial value explicitly.
 Flutter
Flutter 



A new mobile app SDK to help developers and designers build modern mobile apps for iOS and Android. Flutter is an alpha, open-source project.
Documentation
- Main site: flutter.io
- Install
- Get started
- Contribute
Fast development
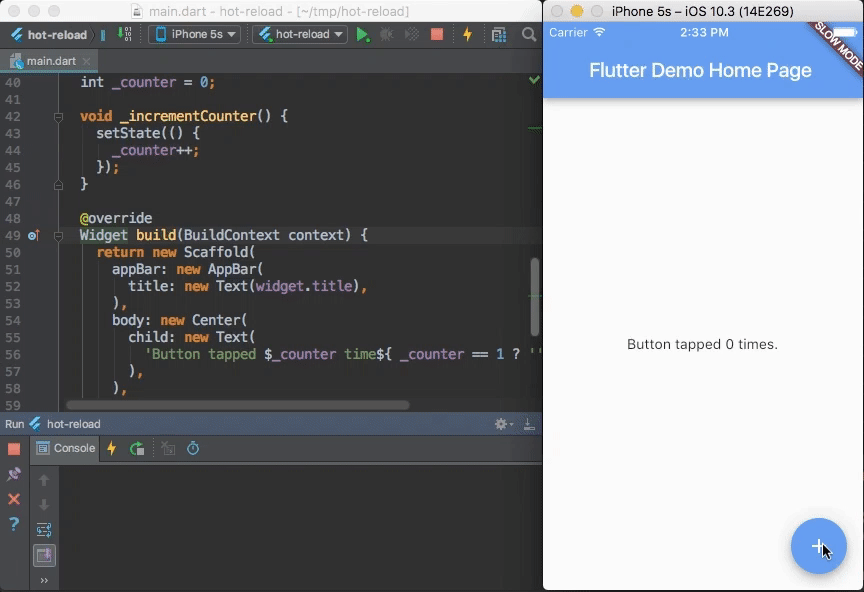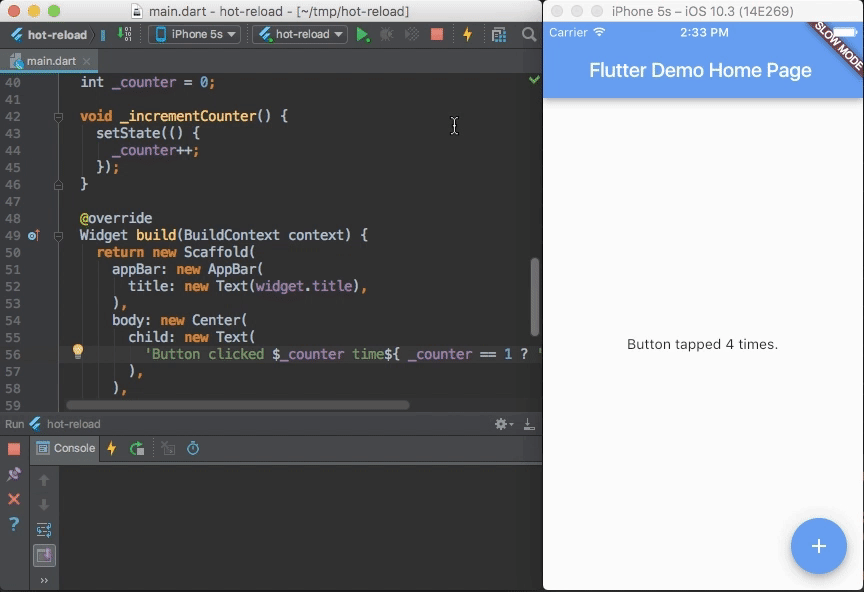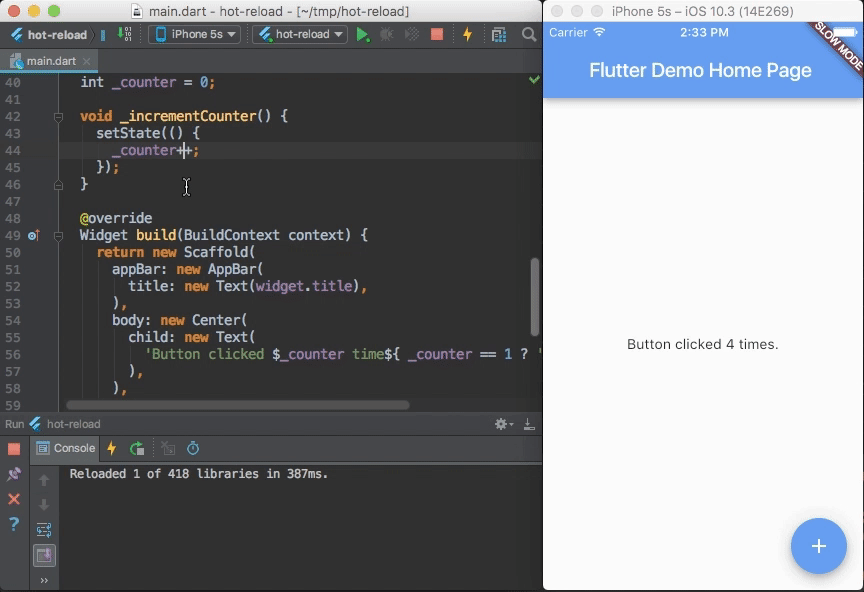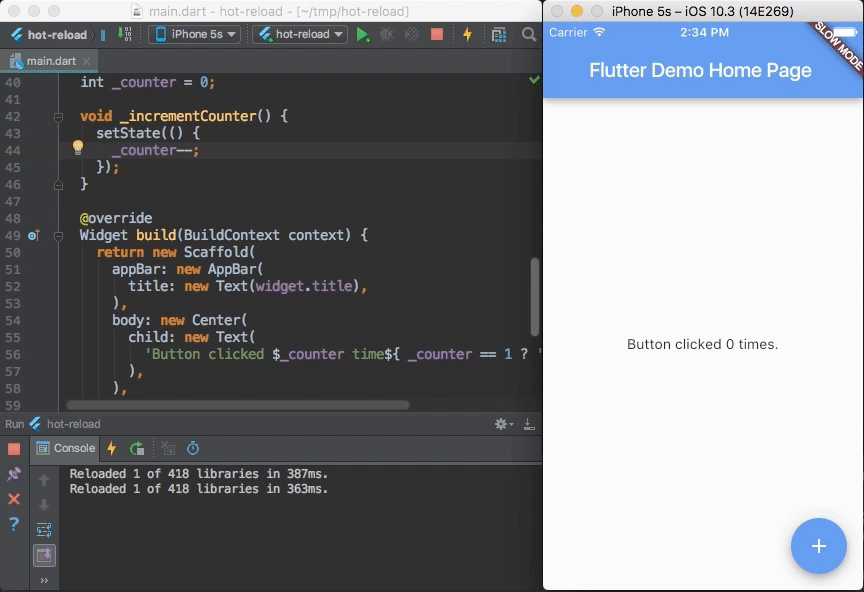
Flutter's hot reload helps you quickly and easily experiment, build UIs, add features, and fix bugs faster. Experience sub-second reload times, without losing state, on emulators, simulators, and hardware for iOS and Android.
Expressive, beautiful UIs
Delight your users with Flutter's built-in beautiful Material Design and Cupertino (iOS-flavor) widgets, rich motion APIs, smooth natural scrolling, and platform awareness.




Browse the widget catalog.
Modern, reactive framework
Easily compose your UI with Flutter's modern functional-reactive framework and rich set of platform, layout, and foundation widgets. Solve your tough UI challenges with powerful and flexible APIs for 2D, animation, gestures, effects, and more.
class CounterState extends State<Counter> {
int counter = 0;
void increment() {
// Tells the Flutter framework that state has changed,
// so the framework can run build() and update the display.
setState(() {
counter++;
});
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called.
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning
// build methods fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that
// needs updating rather than having to individually change
// instances of widgets.
return new Row(
children: <Widget>[
new RaisedButton(
onPressed: increment,
child: new Text('Increment'),
),
new Text('Count: $counter'),
],
);
}
}
Browse the widget catalog and learn more about the functional-reactive framework.
Access native features and SDKs
Make your app come to life with platform APIs, 3rd party SDKs, and native code. Flutter lets you reuse your existing Java, Swift, and ObjC code, and access native features and SDKs on iOS and Android.
Accessing platform features is easy. Here is a snippet from our interop example:
Future<Null> getBatteryLevel() async {
var batteryLevel = 'unknown';
try {
int result = await methodChannel.invokeMethod('getBatteryLevel');
batteryLevel = 'Battery level: $result%';
} on PlatformException {
batteryLevel = 'Failed to get battery level.';
}
setState(() {
_batteryLevel = batteryLevel;
});
}
Learn how to use packages, or write platform channels, to access native code, APIs, and SDKs.
Unified app development
Flutter has the tools and libraries to help you easily bring your ideas to life on iOS and Android. If you don't have any mobile development experience, Flutter is an easy and fast way to build beautiful mobile apps. If you are an experienced iOS or Android developer, you can use Flutter for your views and leverage much of your existing Java/ObjC/Swift investment.
Build
- Beautiful app UIs
- Rich 2D GPU-accelerated APIs
- Reactive framework
- Animation/motion APIs
- Material Design and iOS widgets
- Fluid coding experience
- Sub-second, stateful hot reload
- IntelliJ: refactor, code completion, etc
- Dart language and core libs
- Package manager
- Full-featured apps
- Interop with mobile OS APIs & SDKs
- Maven/Java
- Cocoapods/ObjC/Swift
Optimize
- Test
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- On-device testing
- Debug
- IDE debugger
- Web-based debugger
- async/await aware
- Expression evaluator
- Profile
- Timeline
- CPU and memory
- In-app perf charts
Deploy
- Compile
- Native ARM code
- Dead code elimination
- Distribution
- App Store
- Play Store
Learn more about what makes Flutter special in the technical overview.
Join us in our Gitter chat room or join our public mailing list, flutter-dev@googlegroups.com.